If you are someone who loves to take full control over your android device, you must have probably heared about the term “rooting”. The sole purpose of this article is to shed some light on android rooting, its pros and cons, and its relevance in the present scenario. As an introductory note, the author of this article assumed that his readers are aware about the very basic Android/Linux terminologies.
Table of contents
Moreover, despite the fact that the author is a root user, this article is not at all intended to promote or demotivate a reader from rooting. The intention is rather to explain the merits and demerits of the same for both normal and advanced users by taking a neutral position.

What is Rooting?
Technically, rooting, which is considered as an illegal activity by most, if not all the mobile manufacturers (OEMs), is a process of gaining superuser access over the android ecosystem. As you probably know, a Linux system offers superuser (su) rights to advanced users, which makes them capable of doing a whole bunch of tasks that are natively unavailable for normal users.
As an operating system using a modified Linux Kernel as a base, android also has the exact same feature, which is, however, disabled by default by all the OEMs on their production builds. It is definitely logical by considering the fact that the superuser power on the hands of a noob user is as dangerous as a virus on a human body. For example, a root user can easily manipulate system properties, or in the worst case can delete some of the essential system files that are not even accessible for normal users.
On the other hand, the superuser privileges on an experienced hand will make them capable to do anything on an android device. Imagine, you bought a latest flagship and your OEM provides your device with a number of nonsense system apps (and so non-removable) that you likely never use in your whole life.
Android Rooting: Pros and Cons
Root access will make you capable of removing any system apps, either on a root shell, or by using a suitable third party application. If you are lucky enough with community development support, it is also possible to replace the entire operating system with a custom one made for your device. Thanks to the open source nature of android, the majority of the popular android devices available on the market holds a strong and very active alternate development support, though most of the normal users are either unaware or ignorant of it. * The above-mentioned alternate development includes, but not limited to
- Custom ROMs (fully replaces the stock firmware)
- Custom Kernels (add useful features to an android device by injecting a modified kernel)
- Various modules to do tasks that are not supported natively by an OEM, etc.
Another important scenario is to improve the overall efficiency of an android device, or extend the battery life by tweaking some of the kernel parameters with the help of a powerful kernel manager application, which are also beyond the scope of a non-rooted user. SmartPack-Kernel Manager, an extremely powerful kernel management application provided by the author of this article, is a good example of this kind.
Historically, rooting on various android versions is achieved by utilizing one or more of the exploits found on the source code to inject su binary to the /system/bin or /system/xbin directory. The evolution of projects, such as SuperSU and Magisk by community developers makes rooting much easier for most devices. Later, the active development, open source nature, and system-less behaviour of Magisk makes it as the favorite root solution for most root lovers. Moreover, gaining root access on many devices are as simple as sending a few commands on fastboot or flashing a simple zip file.
Pros & Cons
Now, let’s discuss the pros and cons of rooting on modern devices. We will start with the CONS. As previously mentioned in the article, rooting will give a user the ultimate power on an android device. This is, however, totally against the normal behavior of a Linux-based eco-system as rooting allows a user to interact with the top-level system files or data files owned by other users.
The above mentioned restrictions to access the system properties as well as other user’s data files played an important role to make a Linux based operating system as safe as it is today. As a result, it is very likely that a malicious software installed on a rooted device silently steals or manipulates the sensitive data of a noble user. As an example, an application enjoying root privileges can read and write almost any part of an android device’s storage even on modern devices, whereas a normal user application requires storage write permission to be granted by individual users, provided the device is running on Android 6 (Marshmallow) or above.
Also, accidental or intentional removal of some of the system properties will leave an android device completely useless, either temporarily or permanently in the worst scenario. It is also worth mentioning that a number of popular android applications, especially banking and other online payment interfaces may not work on rooted devices due to the restrictions imposed by their developers.
Moreover, boot loader unlocking, an essential process that should be done to gain root access on most modern devices, will certainly void the manufacturer’s warranty.
Despite the above mentioned cones, the ultimate control over an android device achieved by rooting offers infinite opportunities to a power user. Some of the Pros are listed below.
- Replace the entire firmware provided by the device manufacturer with a completely new one. It will open up unique opportunities for users to enjoy latest android releases on their relatively old devices in which the official updates from the respective OEMs are most likely unavailable.
- Use a kernel manager to manipulate kernel parameters for an improved performance or extend battery life (better user experience in general).
- It is even possible to replace the stock kernel provided by an OEM with a custom one to achieve more kernel-level features. Some of the much loved features offered by custom kernels includes, but not limited to
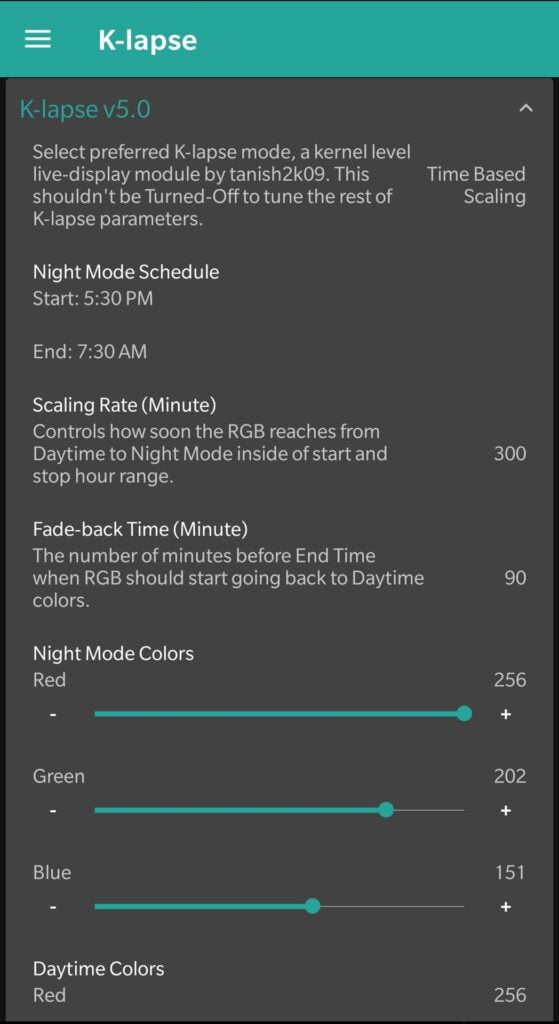
i. K-lapse – a linear RGB scaling module that ‘shifts’ RGB based on time or brightness. ii. Boeffla generic wakelock blocker – a kernel driver to disable wakelocks. iii. USB fast charge – increase charging speed of a device when connected via USB port.
- Easily remove unwanted system applications, either in command-line or by using a third party application.
- Customize almost every part of an android device (example: a custom boot screen).
- Installing an OEM specific application on a device made by another OEM.
- Installing a Magisk or Xposed modules to bring the customization on your device into another level.
- Many more
On the other hand, the approach of most OEMs changed a lot during the past years. For example, fast charging, under various brand names is now supported natively by most OEMs and thereby makes the above-mentioned USB fast charging an obsolete feature. Also, despite the limited capabilities in comparison with the advanced RGB scaling modules, such as K-lapse, many OEMs started providing native features to tweak the RGB scaling on their modern devices. Additionally, the new restrictions and root-level changes introduced by google and different OEMs on each major android update also prevent many users from rooting their expensive flagship devices.
Conclusion
Now, the important question to be answered is whether rooting is still required on modern devices. Unfortunately, there is no generalized answer for this question. Rather, the answer is most likely user specific. A power user, who loves to take full advantage of an android device, will definitely go ahead with rooting. Conversely, rooting may not be the cup of tea of a normal user, who only uses his expensive and precious flagship device for basic tasks, such as making a phone call, texting on WhatsApp, and watching random videos on YouTube.